The world is waking up to the devastating effects of climate change and businesses are feeling the heat to shrink their carbon footprint. Yet, reaching carbon neutrality can seem like an insurmountable task, leaving many companies searching for more viable ways to offset their emissions. Analytics can play a vital role in enabling companies to credibly monitor and assess their carbon footprint and pinpoint where they can make the most significant reductions.
According to a 2022 report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPPC), reaching net-zero emissions by 2050 requires a yearly decrease of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 7.6% starting in 2021, which will result in a 50% reduction by 2030. The active participation of both states and citizens is crucial in raising awareness of the pressing nature of climate change and formulating policies that support climate action.
However, attaining this goal is not a straightforward task and calls for a multifaceted approach incorporating both short- and long-term strategies and implementing various measures. While carbon offsetting can play a critical role, it can be difficult to know where to begin. Here, we outline practical steps that businesses can take to bridge the gap and offset their carbon impact.
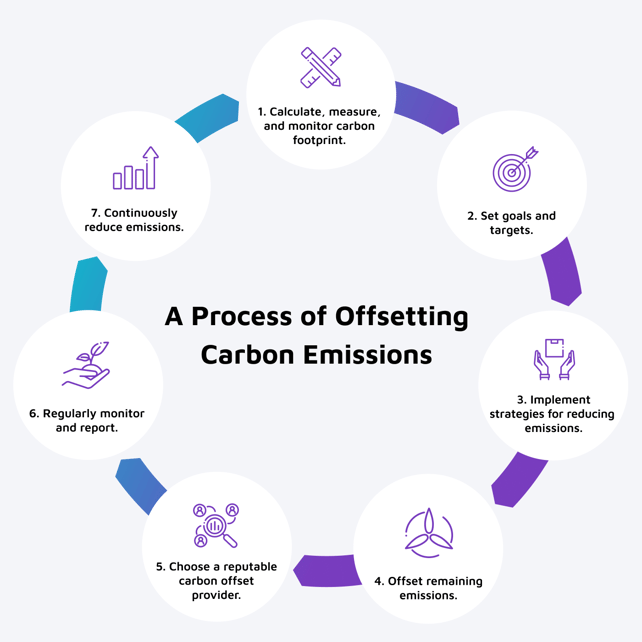
An overview of the continuous process of offsetting carbon emissions
What can a business do to offset their carbon emissions?
Here are the steps that an organization can follow to offset its carbon emissions:
-
Calculate, measure, and monitor carbon footprint. The first step in offsetting carbon emissions is to accurately measure and track the emissions generated by the organization. This information is crucial to determine the extent of emissions that need to be reduced to achieve carbon neutrality. Organizations can follow specific protocols in calculating and measuring their emissions, such as the GHG Protocol, which is a globally accepted standard for measuring and managing GHG emissions. This protocol categorizes emissions into:
-
Scope 1. These are direct emissions from sources that the organization controls.
-
Scope 2. These are indirect emissions generated from purchased electricity, heat, and cooling.
-
Scope 3. These are other indirect emissions from the organization's value chain.
These emissions are quantified in tons of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e), including other GHGs such as methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O).
-
Set goals and targets. After you have a clear understanding of your business’s carbon footprint, set goals and targets to reduce it. This could include a tangible, measurable target over a specific period or a goal to become carbon neutral.
-
Implement emissions reduction strategies. This could include energy-efficient upgrades, the adoption of renewable energy sources, and changes to business processes and supply chain operations.
-
Offset remaining emissions. After reducing your emissions as much as possible, you can offset your remaining emissions by purchasing carbon offsets. These represent a reduction in emissions from another source, such as a wind farm or a forest conservation project.
-
Choose a reputable carbon offset provider. Look for one that is transparent, credible, and have been verified by independent organizations. Look for a partner that offers high-quality offsets that are permanent and verifiable. For example, the United Nations offers a carbon offsetting platform that companies can utilize to determine where to direct their investments.
-
Regularly monitor and report. Make updates as necessary to ensure you're meeting your goals. You should also communicate your carbon offsetting efforts to stakeholders and customers to demonstrate your commitment to reducing your impact on the environment.
-
Continuously reduce emissions. Improve your processes for reducing carbon footprint over time. This could involve investment in new technologies and changes to your business model.
What are the options for calculating and investing in offsetting initiatives?
There are several options for calculating and investing in carbon offsetting initiatives, including:
-
Planting trees. This is a direct approach to reducing carbon emissions, as trees absorb CO2 from the atmosphere and store it in their biomass.
-
Purchasing offset credits. This includes buying credits from carbon offsetting programs, which support renewable energy projects, energy efficiency improvements, or other initiatives that reduce or avoid GHG emissions.
-
Measuring energy efficiency. This involves calculating a company's energy consumption and identifying areas where efficiency improvements can be made to reduce emissions.
-
Getting third-party audits and adopting recommendations. These involve hiring a vetted, independent auditor to assess a company's carbon footprint and make recommendations for reducing emissions and improving sustainability efforts.
-
Adopting carbon offsetting standards. This entails following industry-recognized standards, such as the Verified Carbon Standard or the Climate, Community and Biodiversity Standards, to ensure the offsetting initiatives a company invests in are credible and effective.
Each option has its own advantages and limitations, and it's up to the business to determine which approach is best suited to their specific needs and goals.
.png?width=2728&height=1530&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(22).png)
A sample visualization of an analytics-enabled dashboard for tracking CO2 emissions.
Using analytics toward a credible carbon offsetting initiative
The growing concern over the environmental impact of human activities has encouraged individuals and organizations to take steps to reduce their carbon footprint. Carbon offsetting is a viable means of achieving this goal, as it involves compensating for emissions through measures and activities that reduce or remove CO2.
Integrating analytics into a carbon offsetting strategy provides valuable insights into carbon utilization and identifies areas for improvement. By using and analyzing real-time or near-real-time data, companies can more accurately monitor their emissions, which, in turn, provides more well-informed decisions on energy consumption. Analytics promotes transparency and accountability, which helps organizations avoid the pitfalls of greenwashing.
Lingaro Group provides end-to-end data intelligence that enables enterprises to achieve sustainability and improve the triple bottom line. Lingaro’s supply chain analytics practice works with global brands and enterprises in strategically utilizing data and modern technologies to realize sustainability goals and comply with regulations in ESG reporting. Backed by industry-recognized expertise and powered by AI, Lingaro helps organizations optimize business processes, identify opportunities for improving operations, and mitigate environmental, economic, and social risks in their supply and value chains.
Read more articles on carbon offsetting:
The Business's Guide to Carbon Offsetting
Carbon Offsetting: How It Works and the Benefits for Businesses



.png)



